Balanced Clock Skew Compensation for Immersive Networked Interactions Based on Inter Media Synchronization Level
Abstract
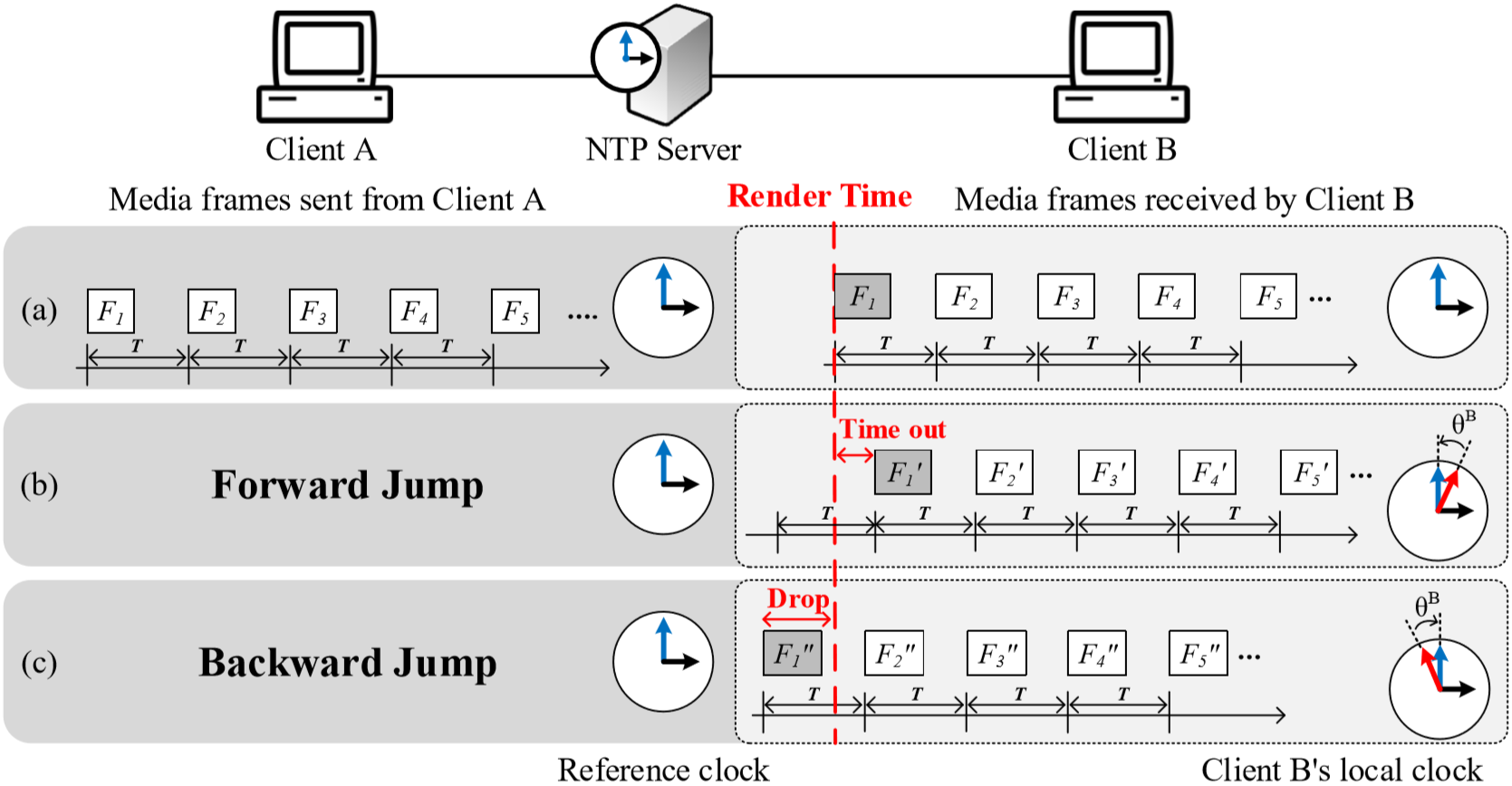
Increasing user presence in networked social applications is an important issue for discussion to increase immersiveness. The feeling of user presence in these applications is determined not only by the types of media it supports – like video, audio, haptics, and motion capture – but also the quality of experience (QoE) in interactivity it provides. When trying to provide high QoE with such heterogeneous media streams, media synchronization is crucial. However, synchronization in itself presents a trade-off between low latency interactivity and media render quality, which are greatly impacted by playout delay and the clock skew compensation frequency, respectively. To balance this trade-off, we propose the Balanced Clock Skew Compensation,a synchronization method that exploits the boundaries for human perception of synchrony, which we define as Inter Media Synchronization Levels (IMSL). The result is a clock skew compensation approach that minimizes forward and backward jumps in media playout, which are detrimental to user perceived QoE, while maintaining low playout delay. User tests with 18 participants show that balanced clock skew compensation is more preferable than fixed frequency clock skew compensation by a large margin for interactive applications.
@inproceedings{lee2018imsl,
author = {Lee, Tae-Young and Lee, Eunmi and Surh, Jaeheung and Lee, Joong-Jae and You, Bum-Jae},
title = {Balanced Clock Skew Compensation for Immersive Networked Interactions Based on Inter Media Synchronization Level},
booktitle = {Proceedings of Computer science and Electronic Engineering Conference (CEEC)},
year = {2018}
}